As the world becomes increasingly digitalized, we are getting closer to data privacy threats. It may be personal data, financial information, or maybe a company’s details everything is at risk of the thankfulness of technological advancement. These rising threats give rise to a new domain of ethical hacking and Cybersecurity. Protecting sensitive information from falling into the wrong hands is one of the most pressing concerns and this concern became an opportunity for ethical hackers and cybersecurity professionals to create a new place in the cyber world. In this ultimate guide about Cybersecurity vs. ethical hacking, we will discuss the differences, advantages, and key certifications, to comprehend both these fields better.
Understanding Ethical Hacking
The term ethical hacking is highly, misapprehended nowadays let’s make it clear first;
“The intentional testing of a system and networks for susceptibility, identifying weaknesses long before any nefarious actors can take advantage is called ethical hacking.”
Its function is performed with the permission of the system owner or setup owner so they are also called white hat hackers as they adopt legal and controlled approaches to improve security.
Key Roles of Ethical Hackers:
- Perform Penetration Tests to Identify Vulnerabilities
- Conduct security assessments to test the defenses of an organization
- Disclose vulnerabilities to strengthen organizational security infrastructure.
Read more about the Ethical Hacking Roadmap You Need for 2024
Understanding Cybersecurity
“A broader field to protect networks, devices and business data form unauthorized attack and destruction by the help of different practices, technologies and polices.”
Our systems are vulnerable to various cyber-attacks so, Cybersecurity professionals are trained in a defensive mood to protect the system and networks from all these threats.
Major Responsibilities of Cybersecurity Professionals:
- Use solutions such as firewalls and anti-virus software.
- Watch these systems for suspicious or malicious activity or abnormal user behavior.
- Create and enforce policies and procedures related to security.
Phases of Cybersecurity
Cybersecurity is not a single process it consists of step-by-step processes that ensure protection from end to end:
- Identification and Assessment: Use assessments to understand current risks/vulnerabilities.
- Protection: This could be through encryption, firewalls, or other network access control measures.
- Detection: The ability to monitor systems to detect anomalous activity.
- Response: which quickly launches an immediate saving operation to prevent and minimize the effects of a break-in
- Recover: Restoring systems and learning from the incident to improve future defenses
These phases form the backbone of how digital assets are secured and protected from anything malicious.
Advantages of Ethical Hacking
Ethical hacking is essential for security within an organization. Here are some benefits:
- Proactive Security: Find and remediate vulnerabilities before a hacker attempts to exploit them.
- Improved Risk Management: Assists companies in focusing their security spending and efforts.
- Data Protection: Ensures compliance with GDPR and HIPAA regulations
- Customer trust: Shows a willingness to keep customer data private.
- Employee Training: Educate your employees about the prevention of social engineering attacks.

Read more about How To Hack WhatsApp Account Ethical Hacking
Ethical Hacking VS Cybersecurity Key Differences
Though both ethical hacking and cybersecurity are important in fighting against cyber threats, they have different terms and methodologies. Here are the main differences:
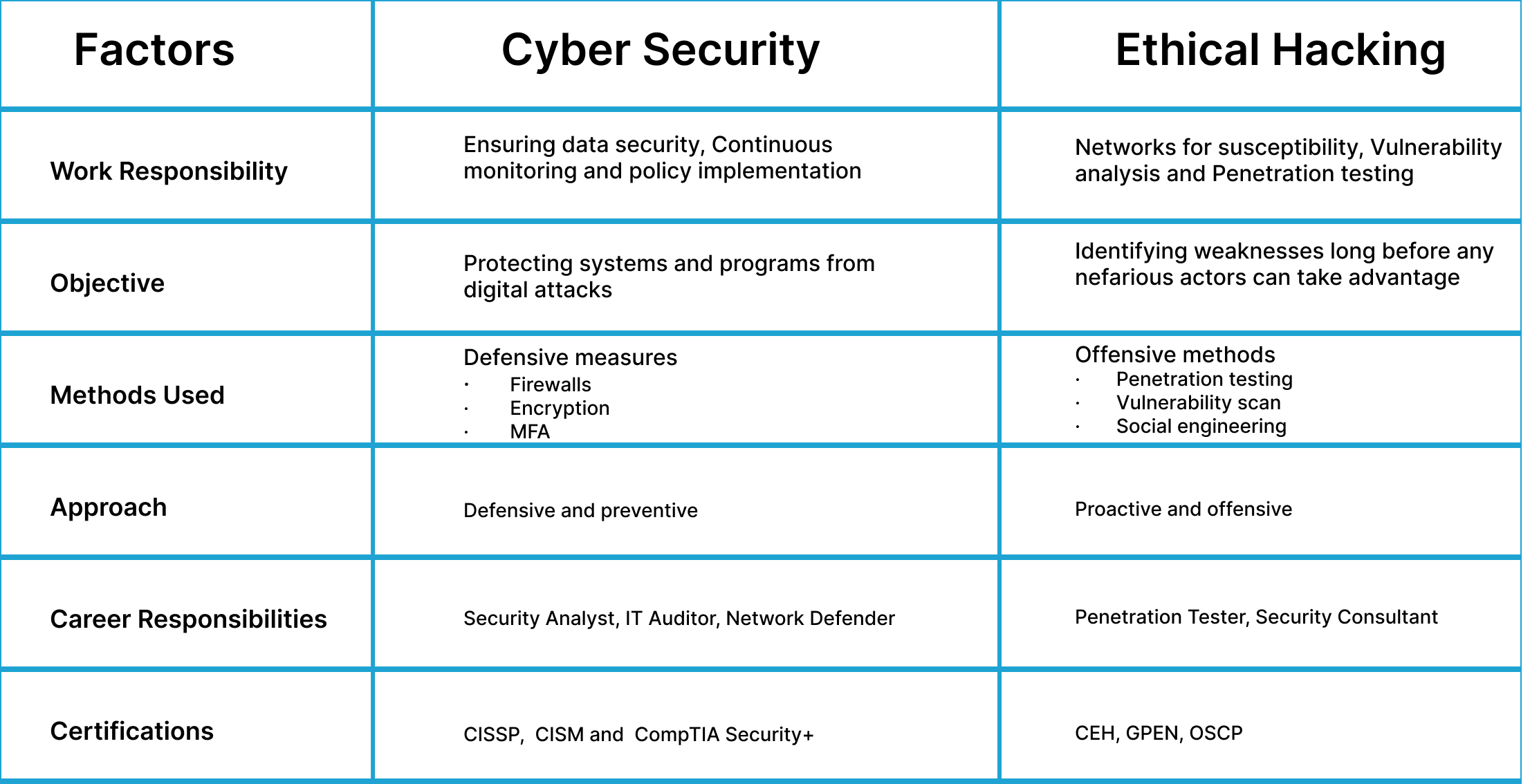
1- Work Responsibility
Ethical Hacking: Primarily concerned with detecting weaknesses through penetration testing and security audits.
Cybersecurity: This includes tactics for preventing a cyber-attack, monitoring networks, and managing the overall security policies.
2- Main Objective
Ethical Hacking: To imitate attacks and identify system flaws before malevolent actors do.
Cybersecurity: The area of securing systems, programs, and networks from cybernetic attacks
3- Methods Used
Ethical Hacking Offensive methods include:
- Penetration testing
- Vulnerability scan
- Social engineering
Cybersecurity for defensive measures includes:
- Firewalls
- Encryption
- MFA
4- Process
Ethical Hacking: Orchestrates pen tests, discovers vulnerabilities, and monitors vulnerability reports to improve security.
Cybersecurity: The practice guarantees the security of the organization’s digital assets through continuous, threat monitoring, policy development, and incident response
A Comprehensive Comparison:
The Worth of Certifications in Ethical Hacking and Cybersecurity
Both fields have certifications that help to increase credibility and employability. They show professionalism and dedication in the field. Following are the certifications that were in most demand:
Best Ethical Hacking Certifications in 2023
- CEH (Certified Ethical Hacker): Specializes in penetration testing and vulnerability assessment.
- The OSCP (Offensive Security Certified Professional) is well-known for exhibiting penetration testing abilities in practical settings.
- The GPEN (The GIAC Penetration Tester ) concentrates on sophisticated penetration testing methods
The Top Certifications in Cybersecurity
- CISSP A broader understanding of security risk management and implementation, aka how to design a security stack.
- CompTIA Security+
- CISM (Certified Information Security Manager): Focuses on managing enterprise data security protocols.
Certifications are plus points and effective cards to boost your earning potential, open up more job opportunities, and gain an edge over rivals in the industry.
Job for Ethical hacking and Cybersecurity
In the analysis of Cybersecurity vs. ethical Hacking, career insight is an important area to cover. Both ethical hackers and cybersecurity professionals are in high demand more precisely they are smashing the average growth rate for other professions. Here are some certifications that might come in handy for those seeking to advance their career within either field:
Job Roles in Ethical Hacking:
- Penetration Tester
- Security Analyst
- Vulnerability Assessor
- Incident Reporter
Job Roles in Cybersecurity:
- Security Consultant
- Network Security Engineer
- Computer forensic analyzer or investigator
- Incident Response Specialist
- Cyber security software developer
AI: Turing point in Cybersecurity and Ethical Hacking
Organizations switching to artificial intelligence (AI) for enhanced defense as digital attacks get more and more worse. So, advancements in AI offer significant benefits for optimizing penetration testing and vulnerability assessments in addition to enhancing threat detection capabilities.
Let us take a closer look at how AI is changing these important domains.
The use of AI in Cybersecurity:
Changing the way we detect Threats Perhaps the biggest benefit of AI in the information security world is its capacity for data analysis, which it can do faster and at a much larger scale than any human or small team ever could. Real-time identification of subtle threats that have a lot of data generated by the networks is quite challenging because traditionally these security systems are lagging in this aspect.
On the other side, machine learning algorithms are trained enough to manage and examine this data to find trends, irregularities, and dangers that human analysts could miss.

Artificial Intelligence in Ethical Hacking:
AI is rapidly integrated into the White Hat hackers community by providing faster and more accurate penetration testing by avoiding human errors. To find potential vulnerabilities in a system or network, ethical hackers usually perform manual penetration tests. But with the AI algorithms, we currently have automated the entire process gives more accurate results and avoids human error.
- AI-powered tools can simulate multiple cyber-attacks in a short period to discover vulnerabilities quicker than manual testing.
- Enter AI a giant leap forward in the penetration testing process that particularly shines when it comes to things like scanning thousands and thousands of network configurations, applications, and systems all at once for vulnerabilities that would take a human weeks or days to find.
- It can also analyze previous attack patterns and predict possible exploits, enabling ethical hackers to preemptively protect the system.
- AI reduces the time for detailed security audits, which typically take thousands of man-hours and are prone to human error. That will not only get ethical hackers’ work done easily, but it also assists organizations to respond faster to security concerns.
The future: embracing symbiosis
The world of ethical hackers and cyber security professionals is going to be changed, as AI technology keeps on advancing. As organizations look to utilize the power of AI tools for digital defenses, the demand for AI expertise in security is rising. Going forward, artificial intelligence can make AI an even more integral necessity, to not only identify and defend against cyber threats but also formulate the plans and technologies deployed by white hat hackers. Having these fields and AI together is revolutionary as it brings an anticipative approach to cyber security and ethical hacking. The collaboration of AI and humans can provide a leading-edge solution for organizations to defend themselves from cybercriminals and enable them to have a secure digital environment.
The Bottom Line:
Cyber security and ethical hacking both play crucial roles in the battle against digital attacks. Cybersecurity VS Ethical Hacking: Which option is best for you will depend on your interests and professional objectives. If finding vulnerabilities by thinking like a hacker is your style, then probably ethical hacking is the best way to go for you. However, if you find yourself gravitating towards strong defense mechanics and securing entire systems, then cyber security may be a better path for you. Both sectors provide well-paying jobs, security, and the ability to influence how secure our digital spaces are.


